Determinants of Scoring in the Mauritius Open
This analysis is based on scores and stats from individual rounds in the seven Mauritius Opens: 3,027 rounds in total. Note that this year's course was used in 2022.
Section 1: Absolute Correlation Coefficients with Score
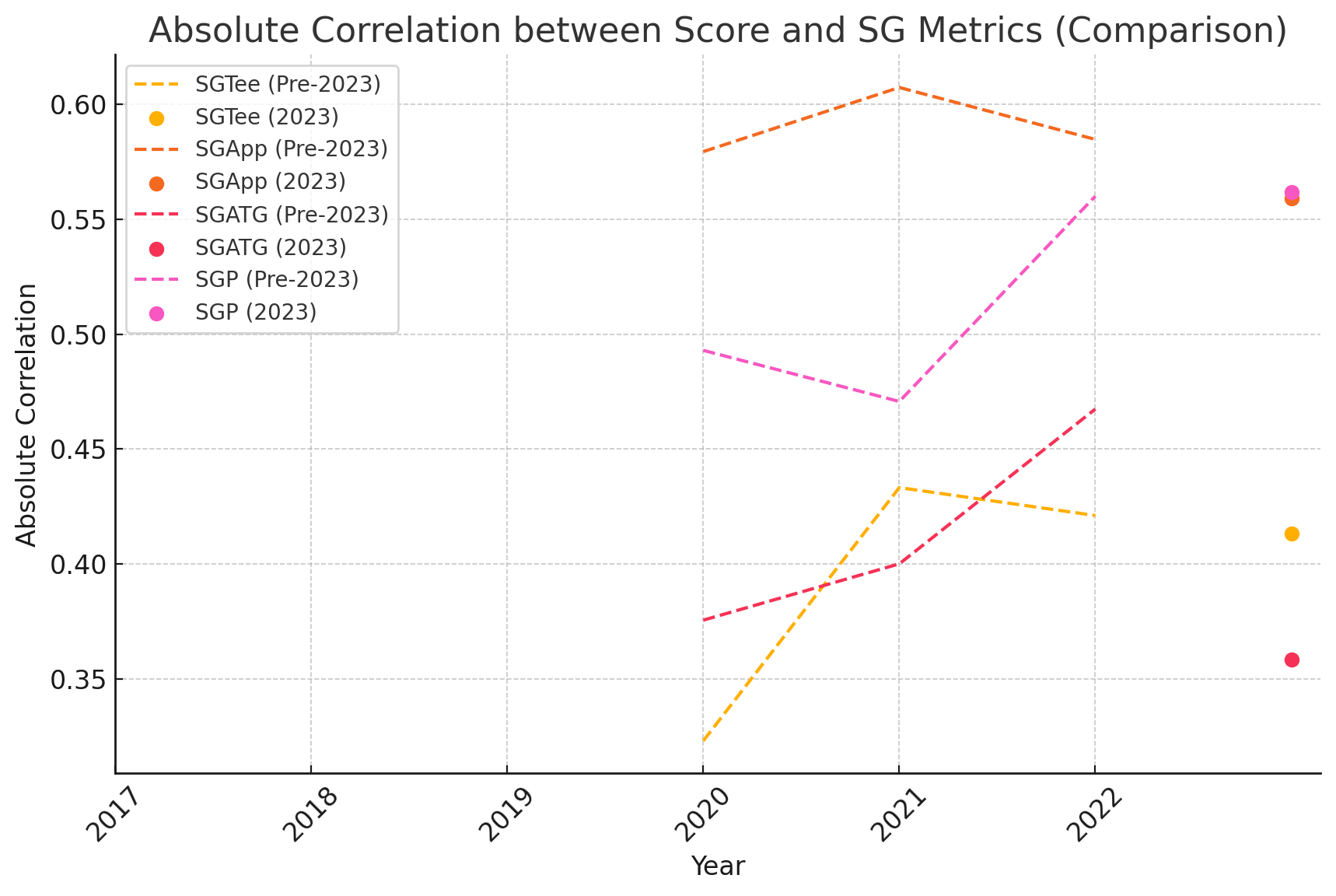
1. SGTee and SGApp: These metrics exhibit a consistently higher correlation with Score across most years, underscoring the importance of tee shots and approach shots in influencing overall performance during tournaments, including the Mauritius Open.
2. SGP: Correlation with putting (SGP) tends to fluctuate year-on-year, suggesting that putting performance varies in its impact, possibly due to course-specific challenges like the greens at the Mauritius Open;
3. SGATG: the lower correlation between this metric and Score suggests a lower significance of short game skills on this course.
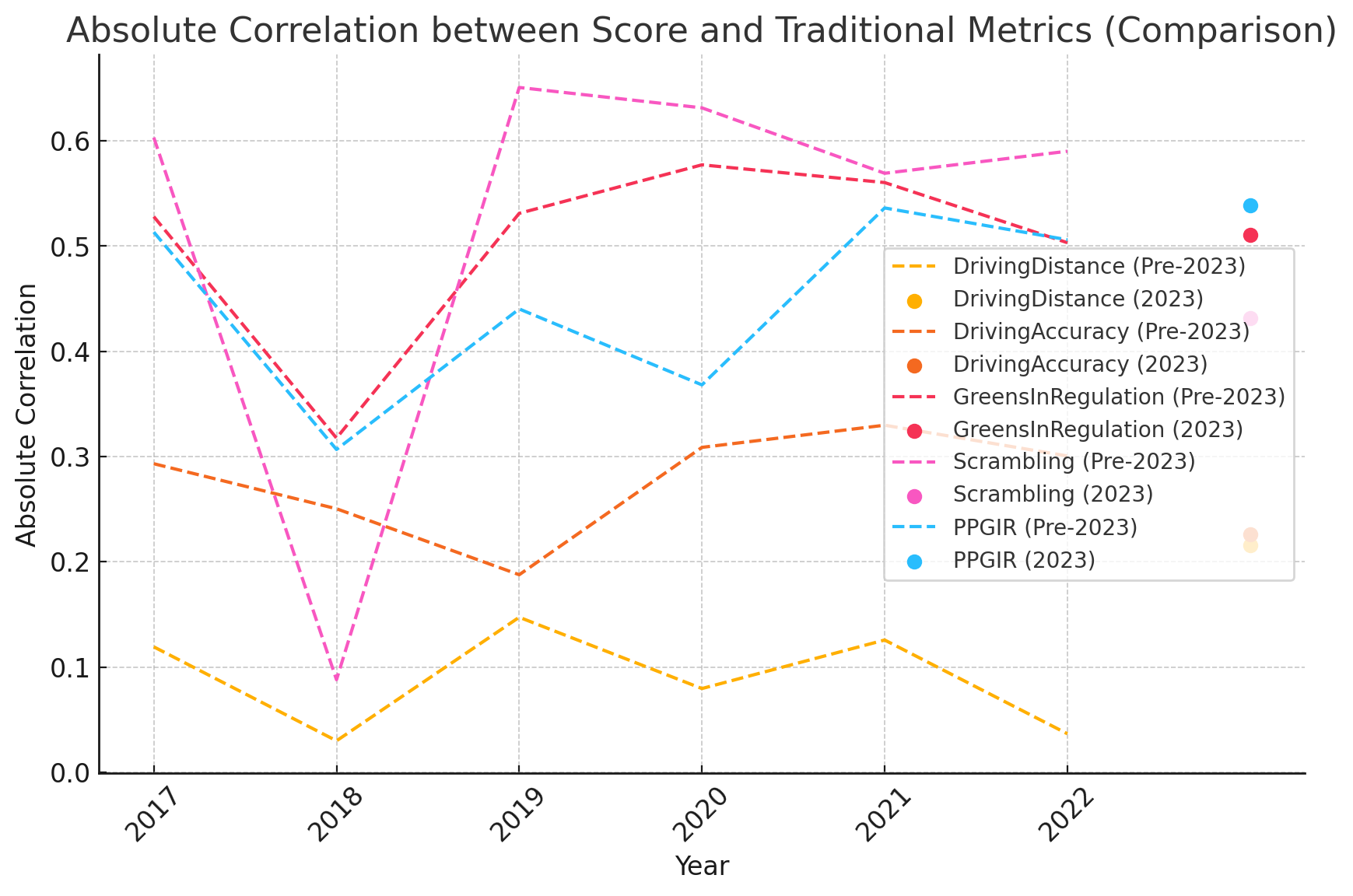
1. Putting Average and Greens in Regulation: These metrics show a relatively stable and significant correlation with Score, reflecting their critical roles in determining performance in the Mauritius Open.
2. Par3 Variability: The correlation for Par3 performance fluctuates more than Par4 or Par5, suggesting that success on Par3s is more course-specific and may be influenced by hole designs at the Mauritius Open.
3. Par5 Scoring: While Par5s generally have a lower correlation with Score, specific years, including Mauritius Open events, exhibit spikes, likely due to opportunities for scoring advantages on reachable Par5s.
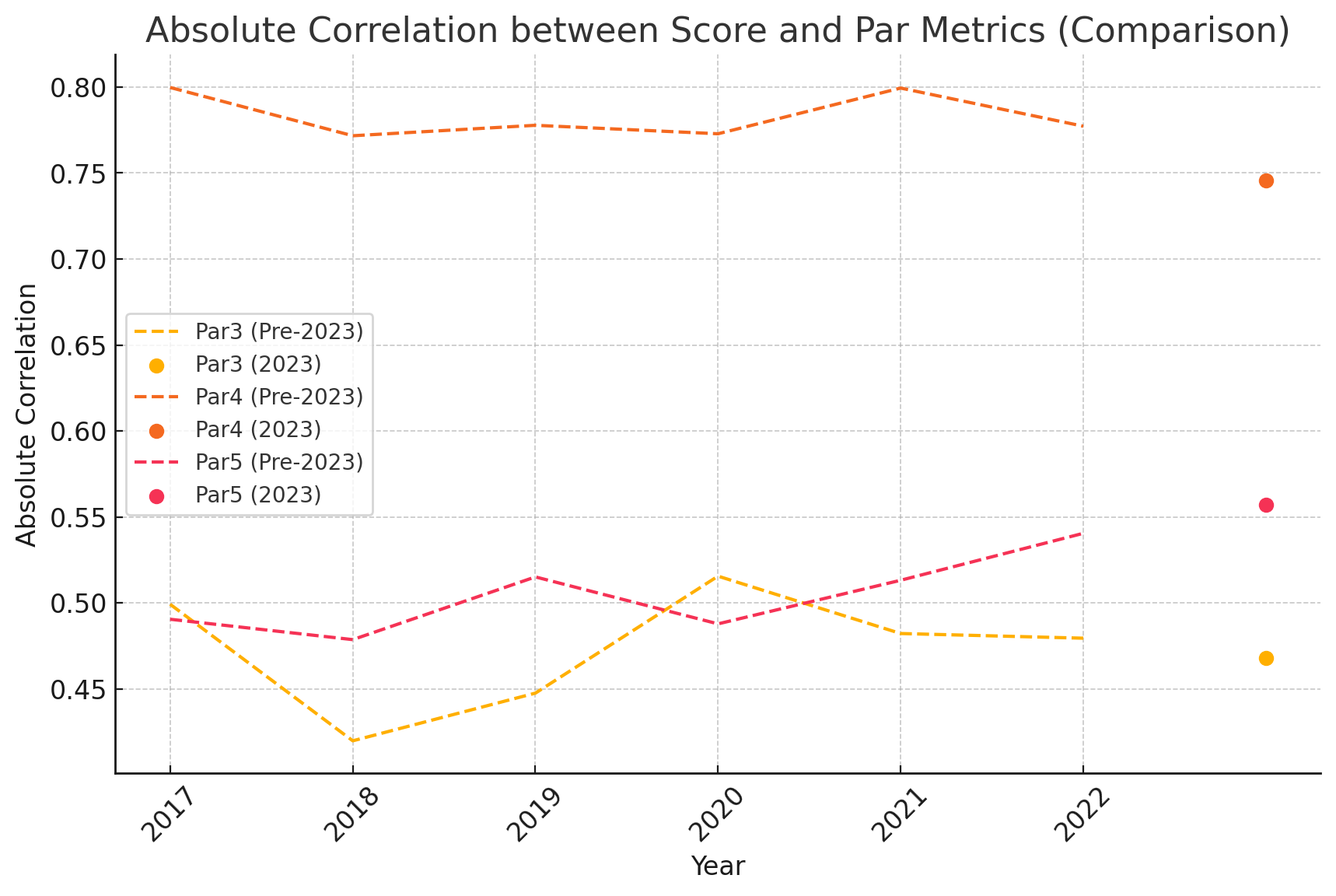
1. Par4 Importance: Par4 metrics consistently show the highest correlation with Score, highlighting their critical role in overall performance. This is especially evident in the Mauritius Open, which features multiple challenging Par4 holes.
2. Fluctuating Impact of Par 5s: Correlations for Par 5s vary significantly, but it notably lowest in 2022.
3. Par 3s Have Lesser Influence: While Par 3s do contribute to the overall score, their correlations are generally lower compared to Par 4 and Par 5 metrics, except for 2022.
Section 2: Importance of Each Metric in Determining Score
Random Forest Regressor and Feature Importance
Random Forest Regressor is an ensemble learning method that constructs multiple decision trees during training and outputs the average prediction. It combines the predictions of several models to improve accuracy and robustness.
Feature importance is a technique used to interpret a machine learning model. It refers to the score that quantifies the contribution of each feature to the prediction made by the model.
In a Random Forest, the importance of a feature is computed by looking at how much the feature decreases the impurity (e.g., variance for regression tasks) across all the trees in the forest. The more a feature decreases the impurity, the more important it is considered.
The calculated importance scores for all features are then normalized to give relative importance as a percentage. This shows the relative contribution of each feature to the prediction task.
Interpreting Feature Importance
Features with high relative importance percentages have a strong impact on the model's predictions. They are crucial for accurate predictions and indicate key areas where performance matters most.
Features with low relative importance have a minimal impact on the model's predictions. While they can still contribute, they are less critical.
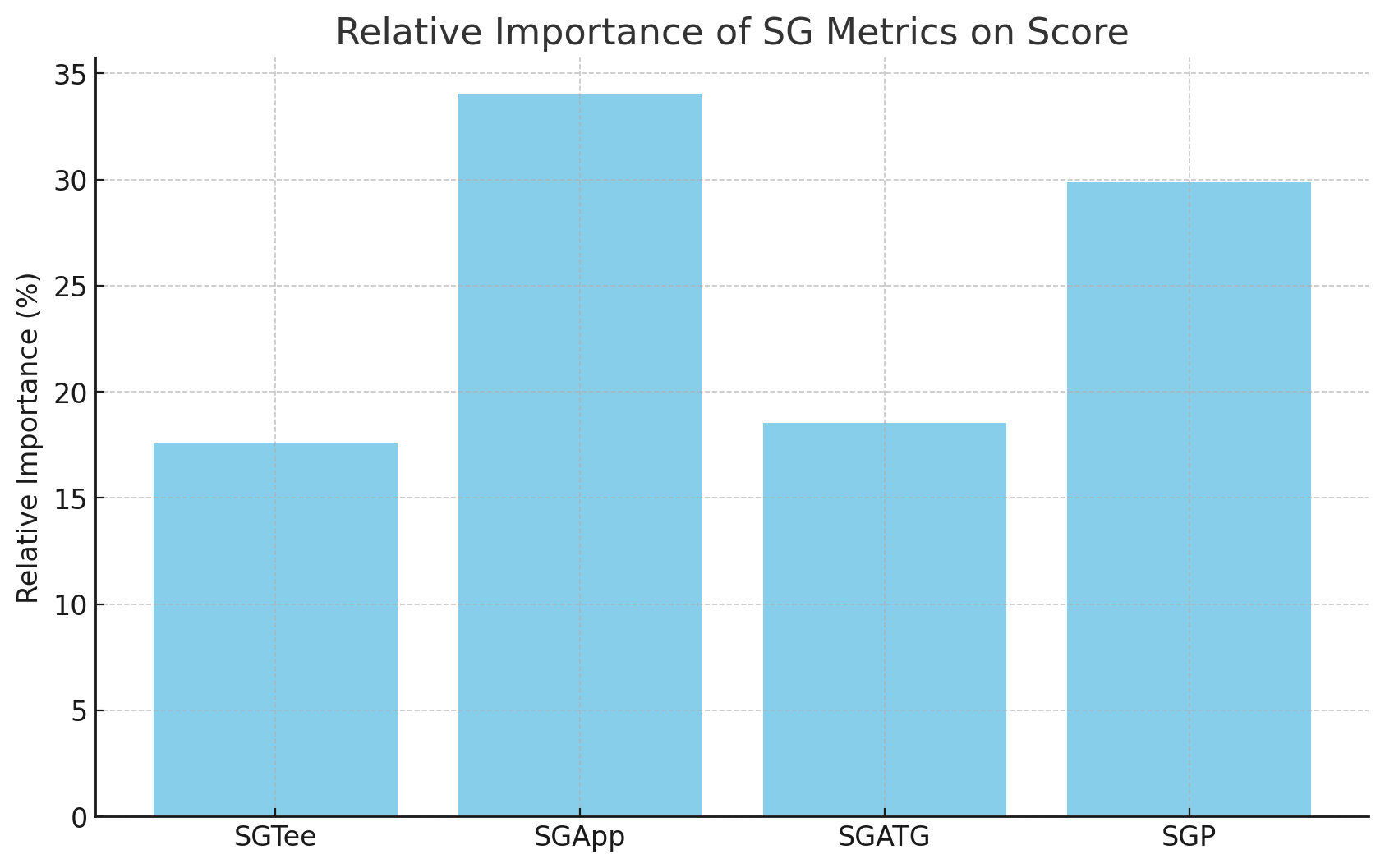
1. SGP Significance: The importance of putting (SGP) is higher than the DP World Tour average of 23.33%, reflecting the critical role of putting on the Mauritius Openís challenging greens.
2. SGTee and SGApp Balance: The relative importances of SGTee (24.15%) and SGApp (27.94%) are closer than the DP World Tour averages, emphasising the need for both accuracy and power off the tee and precision in approach shots at the Mauritius Open.
3. SGATG Lower Impact: The importance of SGATG (18.57%) is notably below the average of 22.45%, suggesting that recovery shots around the green are less pivotal in this tournament.
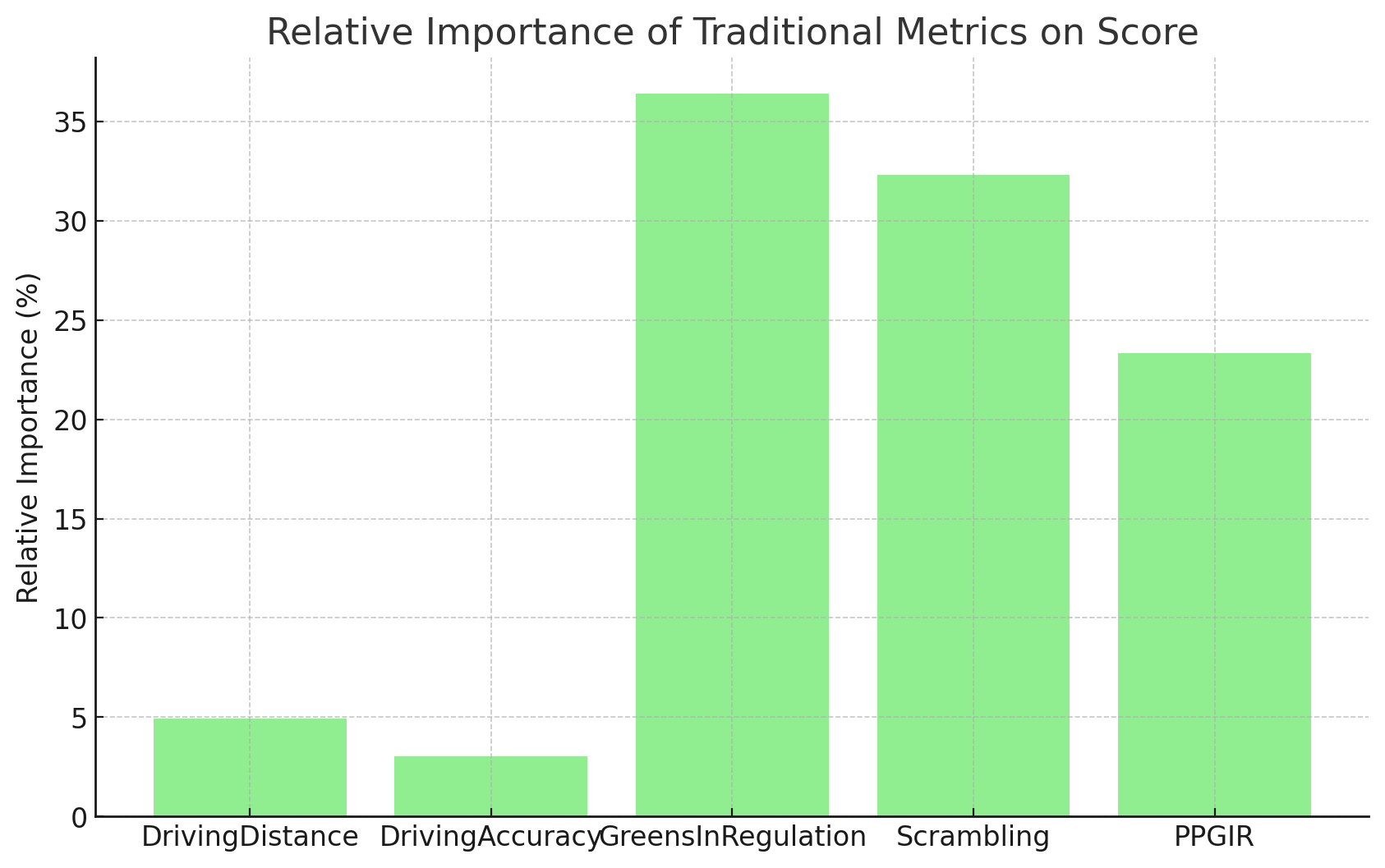
1. Scrambling: At 32.55%, Scrambling stands out as the most critical traditional metric. This reflects the importance of recovery skills in maintaining low scores, particularly on courses with tricky greens or penal rough, such as the Mauritius Open.
2. Greens in Regulation: With a relative importance of 27.34%, this metric remains pivotal, highlighting that consistently reaching greens in regulation correlates strongly with better scoring.
3. Driving Distance vs. Accuracy: While Driving Distance (9.24%) remains more influential than Driving Accuracy (6.83%), the relatively low impact of both metrics indicates that tee shots are less critical to scoring in this event than short game and putting metrics.
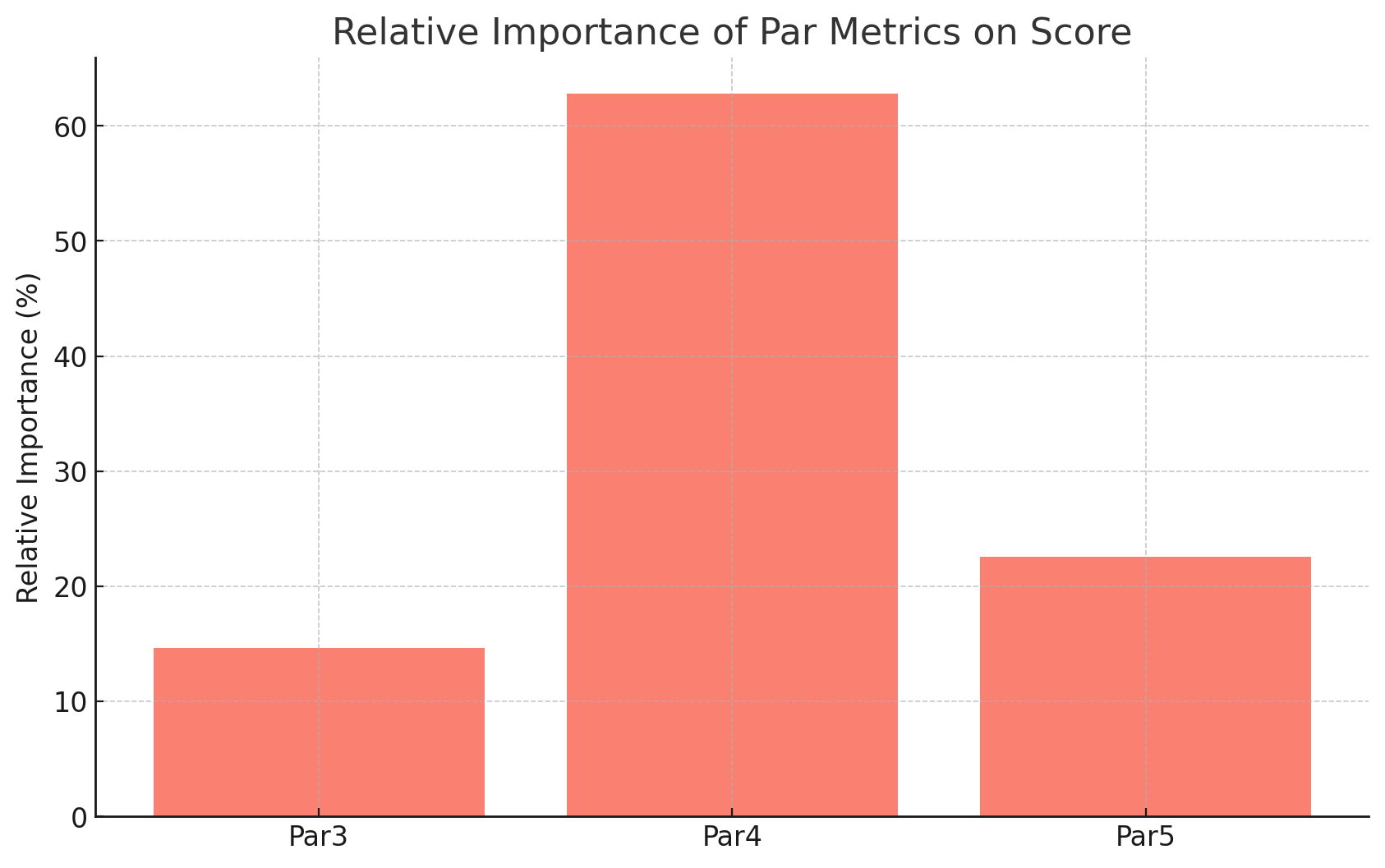
1. Par4 Dominance: Par4 remains the most critical metric, with a relative importance of 51.92%, though this is lower than the DP World Tour average of 64.77%. This indicates that the Mauritius Open's scoring balance shifts slightly toward Par3 and Par5 holes.
2. Par3 Significance: At 21.24%, the importance of Par3 metrics is notably higher than the DP World Tour average of 15.36%, suggesting that Par3 performance is a more significant differentiator in the Mauritius Open.
3. Par5 Opportunities: With an importance of 26.84%, Par5 metrics surpass the DP World Tour average of 19.87%, highlighting the scoring potential of Par5 holes, likely due to reachable greens and birdie opportunities on these holes in the Mauritius Open.
Top 5 Ranked Players - 2024 Nedbank Golf Challenge
The table below shows the top-5 ranked players across the three different Random Forest models above.
| Rank | Surname | Firstname | Average Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Van Tonder | Daniel | 70.05 |
| 2 | Parry | John | 70.18 |
| 3 | Ayora | Angel | 70.35 |
| 4 | Ding | Wenyi | 70.66 |
| 5 | Kruyswijk | Jacques | 70.66 |
Rankings and estimated scores for all players can be found here.