Determinants of Scoring at Tahoe Mountain Club
This analysis is based on scores and stats from individual rounds in the last 4 Tour events at Tahoe Mountain Club: 1,688 rounds in total.
Section 1: Absolute Correlation Coefficients with Score
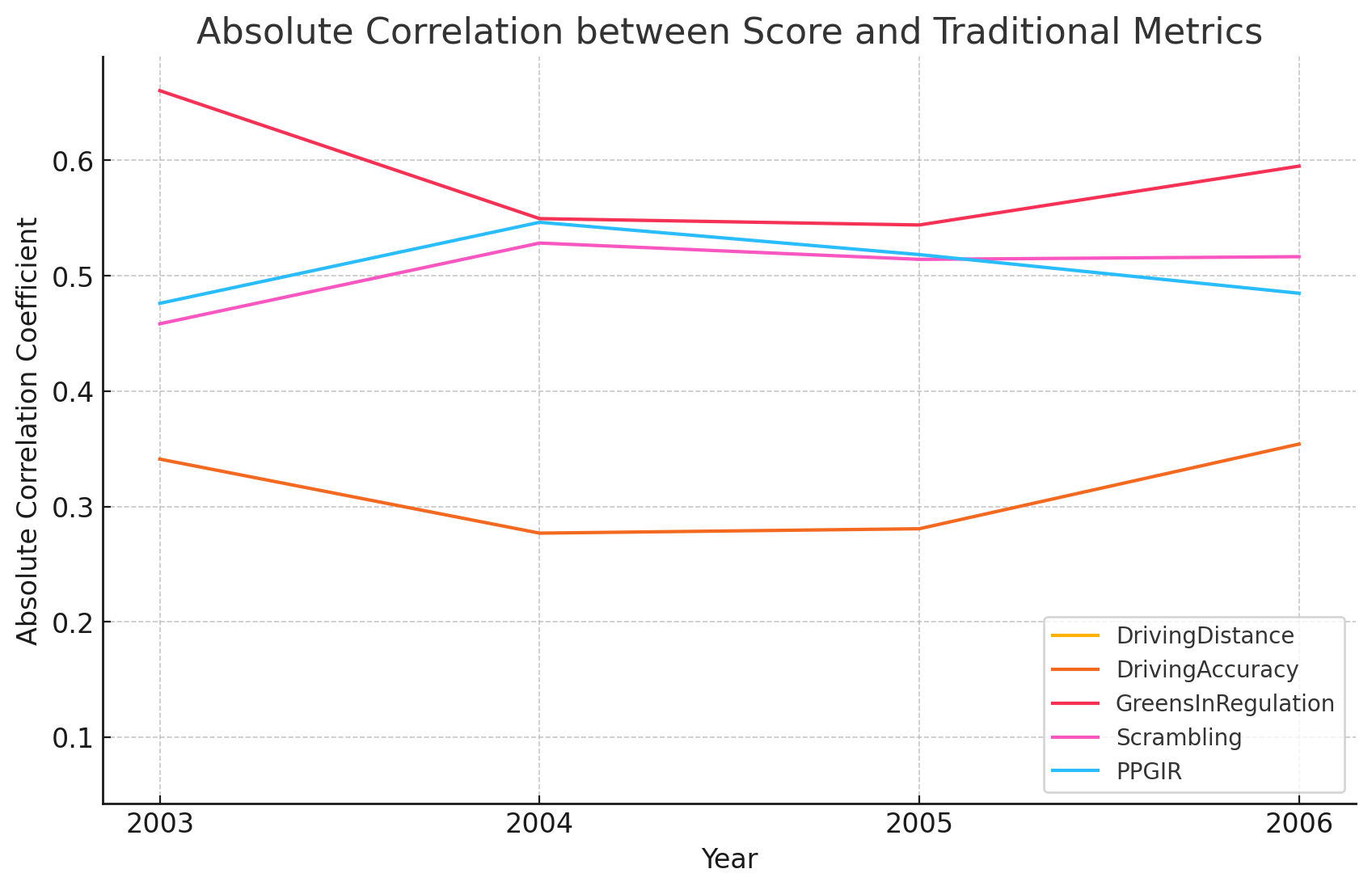
Driving Distance: The absolute correlation between score and driving distance shows minimal variation over the years, remaining relatively low. This suggests that driving distance has not been a strong predictor of scores at Tahoe Mountain Club.
Driving Accuracy: Driving accuracy exhibits a moderate correlation with scores, with some fluctuations over the years. This indicates that players who maintain higher driving accuracy tend to achieve better scores, though the strength of this relationship varies annually.
Greens in Regulation: The correlation between greens in regulation and scores is notably high and consistent. This strong relationship underscores the importance of hitting greens in regulation as a key factor in achieving lower scores at Tahoe Mountain Club.
Scrambling: Scrambling shows a moderate to high correlation with scores, with some yearly variability. This suggests that the ability to recover from missed greens is a significant determinant of scoring performance.
PPGIR (Putts per Greens in Regulation): The absolute correlation for PPGIR is also relatively high, indicating that putting efficiency on greens in regulation is crucial for lower scores. This metric's correlation varies somewhat but remains a strong factor.
The yearly variation in these correlations highlights the dynamic nature of golf performance metrics. While greens in regulation and PPGIR consistently exhibit strong correlations with scores at Tahoe Mountain, other metrics like driving distance and scrambling show more variability.
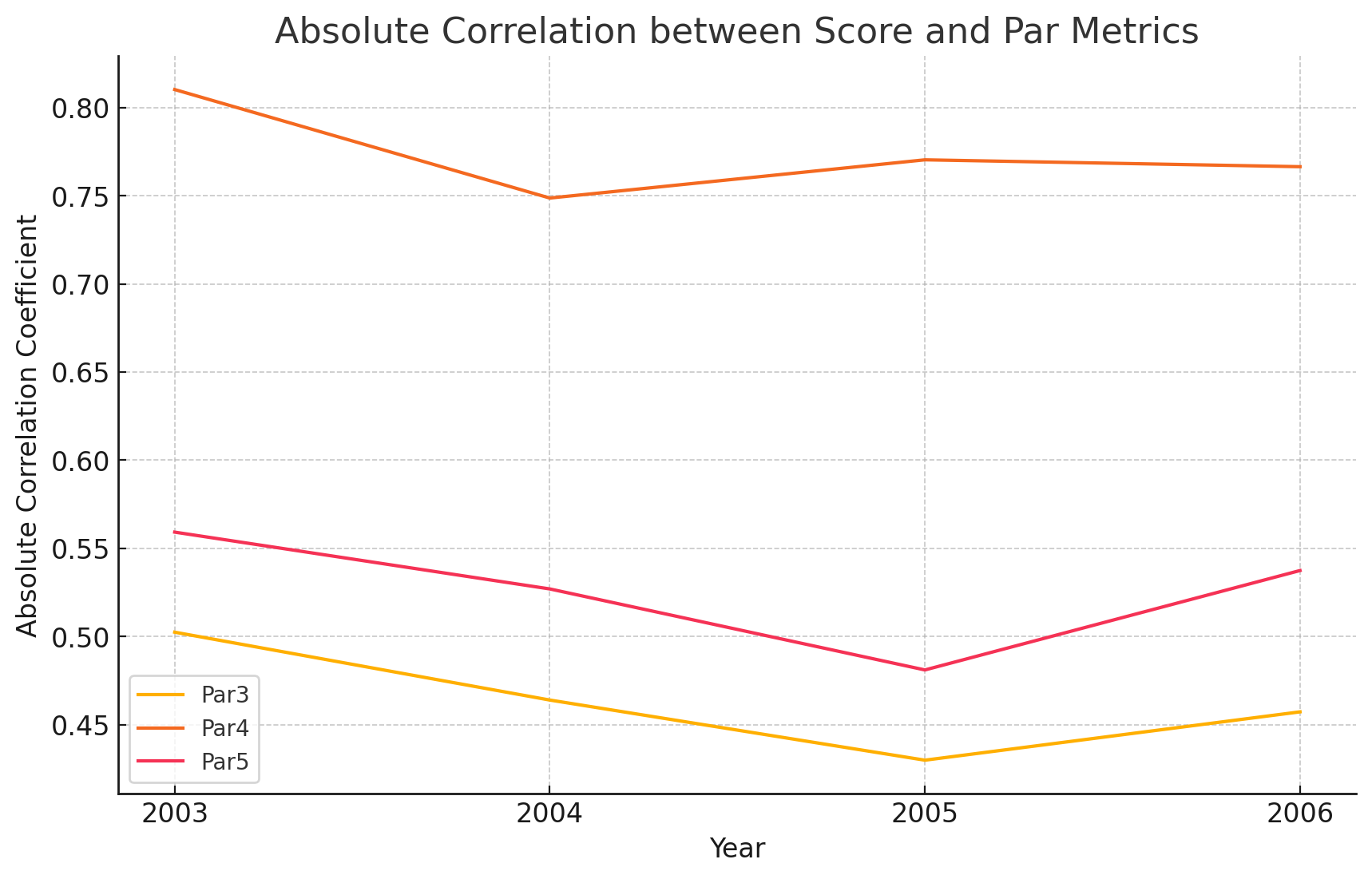
Par 3: The correlation between scores and Par 3 performance is moderately strong, with some fluctuations over the years. This indicates that performance on Par 3 holes is a consistent factor in determining overall scores.
Par 4: Par 4 performance shows a high absolute correlation with scores, highlighting the importance of excelling on these holes. The yearly variation suggests that while Par 4 performance is crucial, its impact can vary based on course setup and conditions.
Par 5: The correlation for Par 5 performance is lower compared to Par 4 performance, but it still shows moderate significance. This suggests that while Par 5 holes offer scoring opportunities, they may not be as critical to overall scoring performance as the Par 4 holes at Tahoe Mountain Club.
The analysis of Par metrics shows that Par 4 performance is consistently the most significant predictor of scores, with less variation compared to Par 3 and Par 5 performance. This stability underscores the importance of maintaining strong play on Par 4 holes to achieve better scores.
Section 2: Partial Dependence Plots against Score
Partial dependence plots (PDPs) are a tool used in machine learning and statistical modeling to illustrate the relationship between a target variable and one or more feature (e.g. SGApp, SGATG, DrivingDistance, GreensInRegulation). They show the marginal effect of a feature on the predicted outcome of a model. PDPs are particularly useful for understanding how individual features impact the target variable, allowing for better interpretation and insights from the model.
In determining the value of Score, PDPs can help visualize how changes in each feature impact the predicted score, holding other features constant. This can provide insights into which features are most influential and how they affect the score.
Driving Distance: The partial dependence plot for driving distance shows a generally flat relationship with score. This indicates that variations in driving distance have a minimal impact on the score at Tahoe Mountain Club, consistent with the low absolute correlation observed earlier.
Driving Accuracy: Driving accuracy exhibits a relationship with score, indicating that maintaining driving accuracy is associated with better performance.
Greens in Regulation: There is a clear relationship between greens in regulation and score. As the percentage of greens hit in regulation changes, the score is significantly impacted. This metric is crucial for low scoring at Tahoe Mountain Club.
Scrambling: The plot for scrambling shows a relationship with score. Players who can effectively recover after missing the green contribute to lower scores, highlighting the significance of a strong short game.
PPGIR (Putts per Greens in Regulation): PPGIR shows a relationship with score, indicating that the number of putts per green in regulation is associated with the score. Efficient putting is critical for maintaining low scores.
The partial dependence plots reinforce the importance of greens in regulation and putting efficiency as key determinants of performance at Tahoe Mountain Club. Driving distance has a minimal impact, while driving accuracy and scrambling skills are moderately important.
Par 3: The partial dependence plot for Par 3 shows a relationship with score. Better performance on Par 3 holes contributes to lower overall scores, but the impact is less pronounced compared to Par 4 and Par 5.
Par 4: Par 4 performance has a clear relationship with score, indicating that excelling on Par 4 holes is crucial for achieving low scores. This aligns with the high absolute correlation observed earlier.
Par 5: The plot for Par 5 shows a relationship with score. Good performance on Par 5 holes helps in lowering the score, although the impact is not as strong as Par 4 performance.
The analysis confirms that Par 4 performance is the most significant factor in determining scores at Tahoe Mountain Club. While Par 3 and Par 5 performances are also important, they have a relatively lower impact on the overall score.
Section 3: Importance of Each Metric in Determining Score
Random Forest Regressor and Feature Importance
Random Forest Regressor is an ensemble learning method that constructs multiple decision trees during training and outputs the average prediction. It combines the predictions of several models to improve accuracy and robustness.
Feature importance is a technique used to interpret a machine learning model. It refers to the score that quantifies the contribution of each feature to the prediction made by the model.
In a Random Forest, the importance of a feature is computed by looking at how much the feature decreases the impurity (e.g., variance for regression tasks) across all the trees in the forest. The more a feature decreases the impurity, the more important it is considered.
The calculated importance scores for all features are then normalized to give relative importance as a percentage. This shows the relative contribution of each feature to the prediction task.
Interpreting Feature Importance
Features with high relative importance percentages have a strong impact on the model's predictions. They are crucial for accurate predictions and indicate key areas where performance matters most.
Features with low relative importance have a minimal impact on the model's predictions. While they can still contribute, they are less critical.
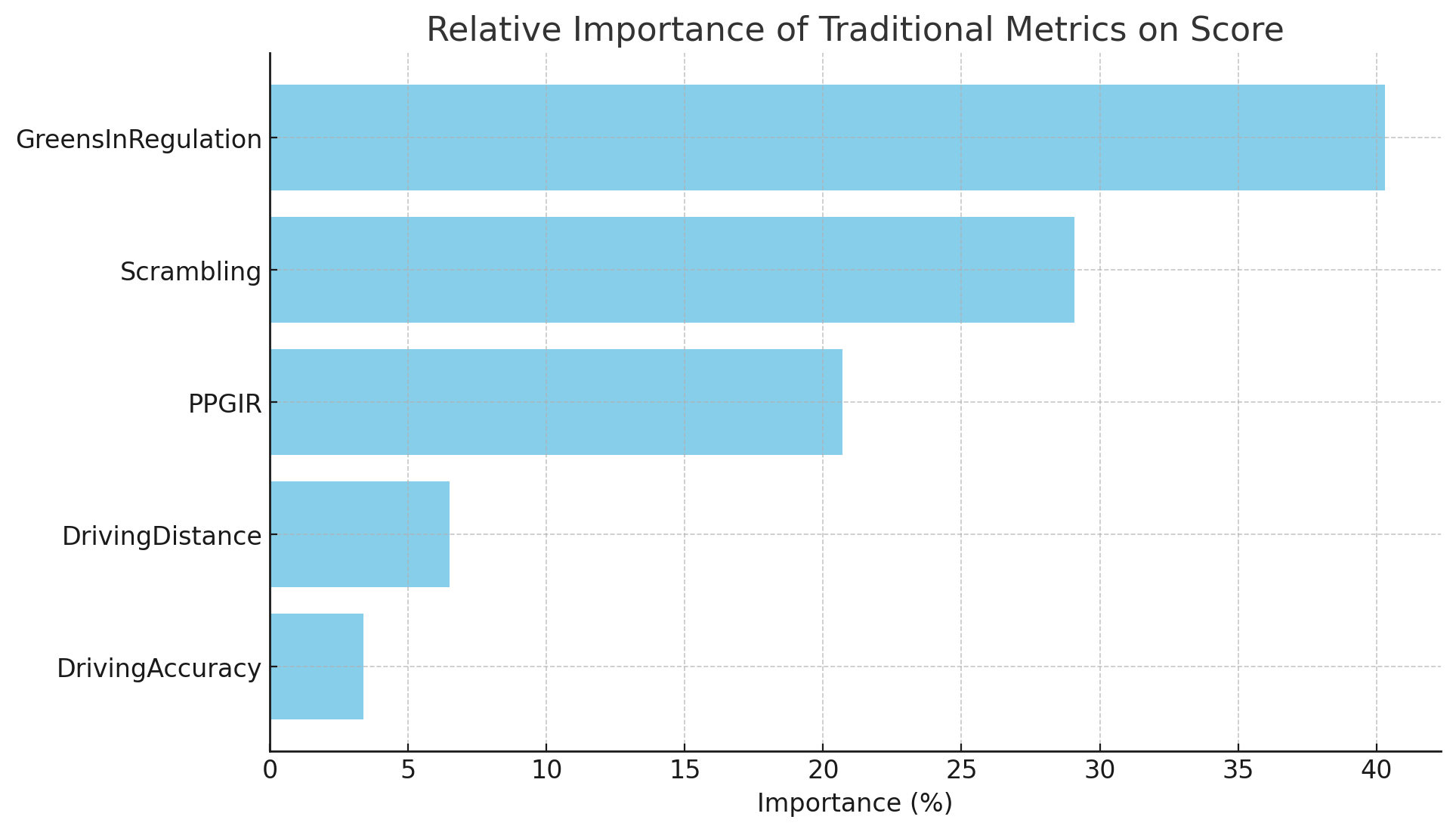
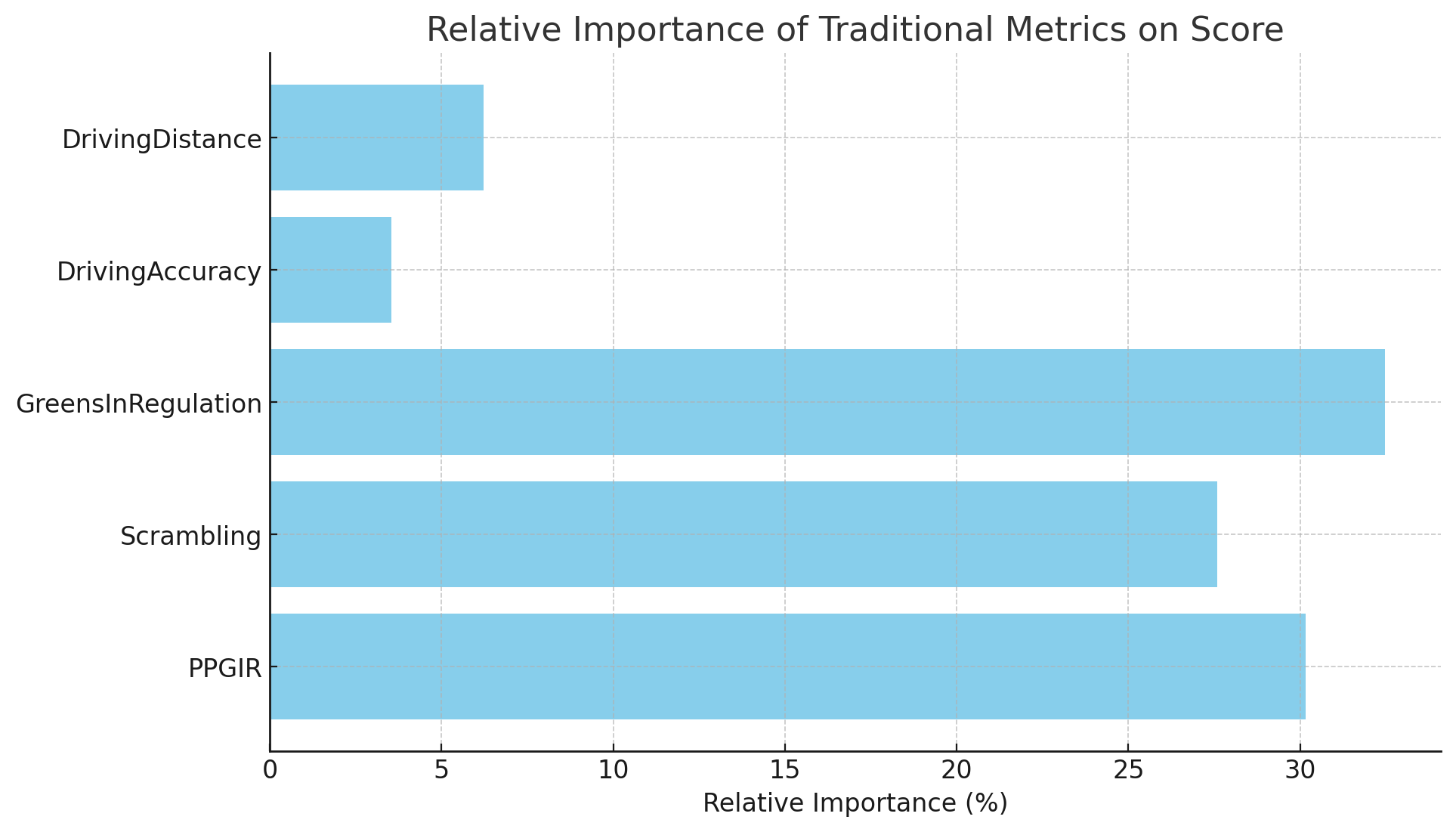
Using a Random Forest Regressor, the relative importance of each factor on the Score is calculated as follows:
- GreensInRegulation: 35.18%
- PPGIR: 29.92%
- Scrambling: 27.25%
- DrivingDistance: 4.47%
- DrivingAccuracy: 3.17%
These results highlight that GreensInRegulation, PPGIR, and Scrambling have the most significant impact on a golfer's score at Tahoe Mountain Club, with GreensInRegulation being the most influential. DrivingDistance and DrivingAccuracy have a relatively minor impact.
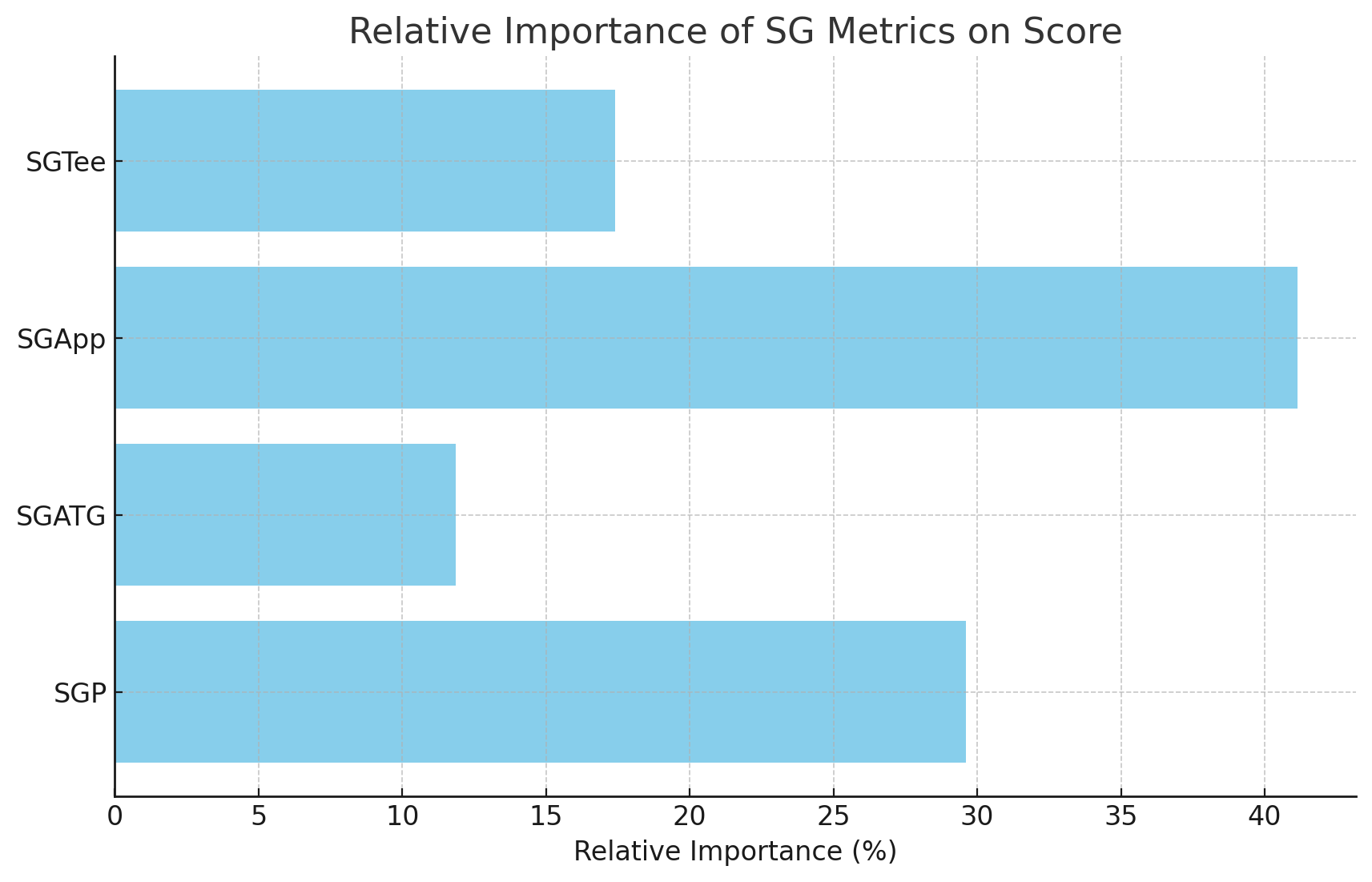
For comparison, here is the relative importance of each factor across all PGA Tour events over the last 10 years:
- DrivingDistance: 9.31%
- DrivingAccuracy: 3.77%
- GreensInRegulation: 29.77%
- Scrambling: 27.02%
- PPGIR (Putts per GIR): 30.13%
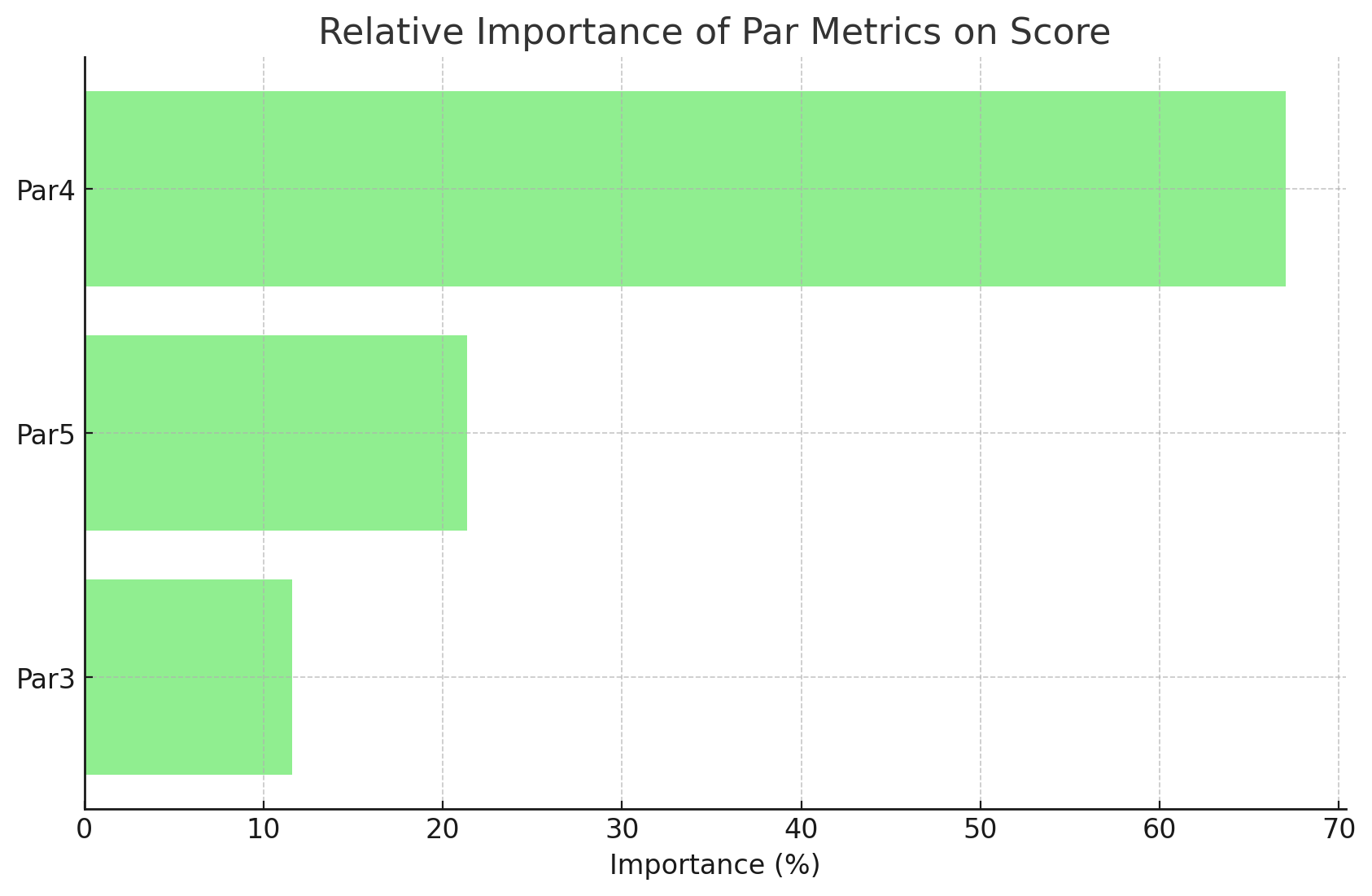
Using a Random Forest Regressor, the relative importance of each factor on the Score is calculated as follows:
- Par4: 66.40%
- Par5: 17.61%
- Par3: 15.99%
The results indicate that performance on Par4 holes is the most critical factor affecting a golfer's score, accounting for around two-thirds of the importance. Par5 and Par3 holes are less influential but still contribute to the overall score, with Par5 having a slightly higher impact than Par3.
For comparison, here is the relative importance of each factor across all DP World Tour events over the last 10 years:
- Par3: 17.32%
- Par4: 67.12%
- Par5: 15.56%
Top 5 Ranked Players - 2024 Barracuda Championship
The table below shows the top-5 ranked players and their average estimated scores from the different Random Forest models above.
| Player | Score |
|---|---|
| Ben Silverman | 68.90 |
| Vince Whaley | 69.25 |
| Michael Thorbjornsen | 69.29 |
| Erik Van Rooyen | 69.42 |
| Martin Laird | 69.47 |
Estimated scores for all players can be found here.